11/12/2024
Flyway for database migrations in Spring Boot applications
Database migrations are a critical aspect of managing evolving software applications. As the application grows, database schemas often need adjustments such as adding tables, modifying columns, or introducing indexes. **F
Database migrations are a critical aspect of managing evolving software applications. As the application grows, database schemas often need adjustments such as adding tables, modifying columns, or introducing indexes. Flyway is a popular tool for handling these migrations seamlessly in Spring Boot applications. This guide will walk you through setting up and using Flyway effectively.
What is Flyway?
Flyway is an open-source database migration tool that allows developers to version-control their database changes. It applies incremental updates to the database schema based on migration scripts. Flyway supports a wide range of databases, including MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQL Server, and more.
Redgate Flyway - Automate database deployments across teams and technologies
Key features of Flyway
- Version control: Tracks each migration with a version number.
- SQL and Java-based migrations: Supports writing migrations in SQL scripts or Java.
- Consistency: Ensures all environments stay in sync.
- Ease of use: Integrates smoothly with Spring Boot.
Setting Up Flyway in a Spring Boot Project
Add Flyway Dependency
To start using Flyway, include the Flyway dependency in your pom.xml for Maven projects:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.flywaydb</groupId>
<artifactId>flyway-core</artifactId>
</dependency>
For Gradle, add:
implementation 'org.flywaydb:flyway-core'
Maven Repository: org.flywaydb » flyway-core
Configure the database connection
Ensure your application.properties or application.yml file contains the database connection details. Flyway uses the same data source configuration as Spring Boot.
For example:
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=org.postgresql.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:6432/mydb
spring.datasource.username=myusername
spring.datasource.password=mypassword
Flyway will automatically detect this configuration and apply migrations on the specified database.
Writing Flyway migration scripts
Flyway uses SQL files (or Java classes) to define migrations. These files are stored in the db/migration directory under src/main/resources by default.
File naming convention
Migration files must follow a specific naming convention:
V<VERSION>__<DESCRIPTION>.sql
- V: Indicates a versioned migration.
- VERSION: Specifies the migration version (e.g.,
1,1.1,2). - DESCRIPTION: Describes the purpose of the migration (use underscores
_instead of spaces).
For example:
V1__Create_users_table.sql
V2__Add_email_to_users_table.sql
Sample migration script
Here’s an example script to create a users table:
CREATE TABLE users
(
id BIGINT UNIQUE GENERATED BY DEFAULT AS IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
username VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR(100),
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT NOW()
);
Place this file in src/main/resources/db/migration.
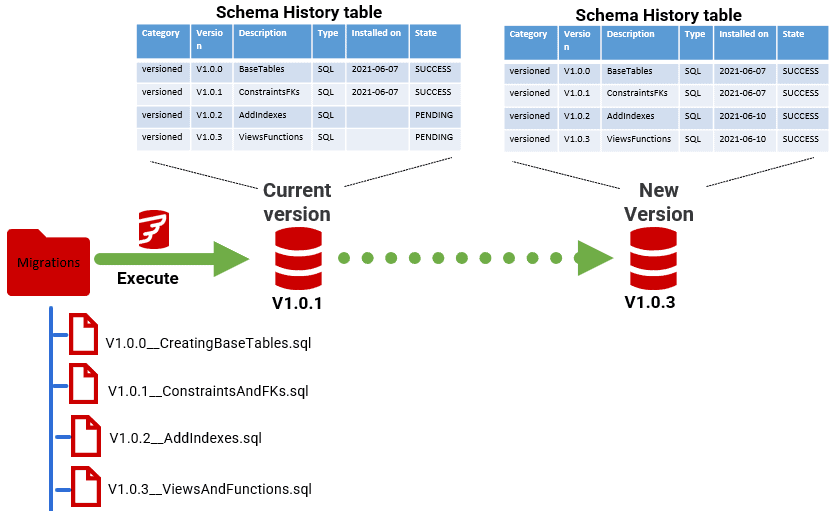
Flyway in action
When you run your Spring Boot application, Flyway will:
- Check the database for an existing
flyway_schema_historytable. - Compare the applied migrations with the available ones.
- Execute any pending migrations in order of their version numbers.
Verifying migrations
You can verify the applied migrations in the flyway_schema_history table, which contains records of all executed migrations, including their versions and execution timestamps.
Advanced Flyway features
Java-based migrations
For complex migrations, you can create Java-based migrations by implementing the Migration interface:
import org.flywaydb.core.api.migration.BaseJavaMigration;
import org.flywaydb.core.api.migration.Context;
public class V3__Update_user_roles extends BaseJavaMigration {
@Override
public void migrate(Context context) throws Exception {
try (Statement statement = context.getConnection().createStatement()) {
statement.execute("ALTER TABLE users ADD COLUMN role VARCHAR(50)");
}
}
}
Place this class in a package that Flyway scans for migrations.
Customizing Flyway configuration
You can customize Flyway behavior in your application.properties:
spring.flyway.locations=classpath:db/migration,filesystem:/external/migrations
spring.flyway.baseline-on-migrate=true
spring.flyway.clean-disabled=true
locations: Specifies migration script locations.baseline-on-migrate: Allows Flyway to baseline an existing database.clean-disabled: Disables the destructivecleancommand for safety.
Handling rollbacks
Flyway doesn’t support automated rollbacks directly. You must manually write a rollback script if needed.
Best practices for Flyway migrations
- Test Scripts Thoroughly: Always test migration scripts in a development environment before applying them to production.
- Version Carefully: Use meaningful version numbers and descriptions to avoid confusion.
- Avoid Breaking Changes: Ensure migrations are backward-compatible, especially in distributed systems.
Example repository for reference
To complement this tutorial, I've created a GitHub repository showcasing an example implementation of the basic spring boot flyway migration script.
briacdev/spring-boot-flyway-poc
Flyway simplifies database migrations, making them reliable and predictable. By integrating Flyway into your Spring Boot application, you can ensure your database schema evolves in sync with your application’s requirements. Follow best practices and leverage Flyway's features to manage your database changes effectively.